How to install qemu-kvm and gui (virt-manager) in Ubuntu
A GNU/Linux user actually can do machine virtualization without using Oracle VirtualBox, by just taking advantage of already included feature of Linux kernel, KVM. KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a kernel module of Linux which enables a GNU/Linux operating system to run virtual machine of another operating system (just like VirtualBox). But because KVM is a part of the kernel (kernel module), it is very lightweight and fast (compared to VirtualBox and VMWare as external things). While KVM works in kernel-space, we use QEMU as the machine emulator for user-space. This QEMU KVM combination gives the users lightweight virtualization and good performance (but with no GUI). We can make it perfect with Red Hat Virtual Machine Manager as the GUI for QEMU KVM virtualization. QEMU, KVM, and Virtual Machine Manager are all free software. We introduce here how to install them in Ubuntu.
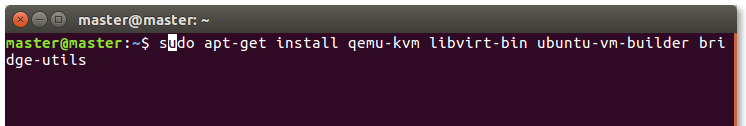
Install KVM
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin ubuntu-vm-builder bridge-utils
qemu-kvmcontains the basic QEMU KVM programslibvirt-bincontains programs for the libvirt library (the library which takes advantage from Linux kernel’s virtualization feature)ubuntu-vm-buildercontains Ubuntu VM Builder scripts (to help creating ready to use virtual machine in Ubuntu)bridge-utilscontains programs to connect your host network to the virtual machine
Install A GUI for KVM
sudo apt-get install virt-manager
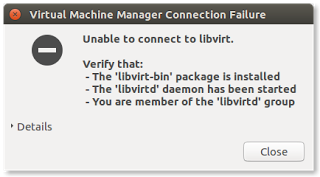
Common Problem
Without relogin, or without adding username into libvirtd group, you may see Virtual Machine Manager error like picture below. If you have followed the rest of article, you just need to relogin.
References
[1] http://www.ubuntubuzz.com/2016/05/how-to-install-kvm-with-gui-virt-manager-in-ubuntu.html